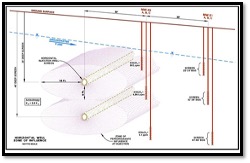
While horizontal drilling techniques offer substantial advantages over vertical practices in terms of physical access to the plume, a more efficient cleanup is also accomplished by expanding the radius of influence (ROI) and closing the remedial gap with horizontal remediation wells. A horizontal well provides significantly more screen contact with the contaminant plume and improves the overall ROI of the remedial efforts by being installed along known preferential pathways instead of transecting them. By expanding the ROI, a larger portion of the contaminant plume is intersected, which results in a faster and more thorough remedial clean-up.
Enhancing the Radius of Influence
Horizontal wells offer several advantages over vertical remediation wells, particularly when it comes to enhancing the radius of influence when addressing subsurface soil and groundwater remediation. Vertical remediation wells are only capable of influencing a limited area within the target formation and rely on the overlapping ROI of adjacent vertical wells to create a uniform interception of the contaminant plume. Confirmation results often reveal the presence of gaps in the remedial zone where contaminants are not fully captured, allowing continued downgradient migration and development of dispersed “hotspots.”
Horizontal remediation wells extend laterally through the contaminated zone, providing maximum contact between the screen interval and the contaminant plume. This enhanced contact ensures a more thorough distribution of remediation efforts as the radius of influence is evenly dispersed along the length of one horizontal screen, versus multiple vertical screens. Horizontal wells also provide flexibility in navigating complex subsurface geologies and avoiding obstructions. Since they can be installed at various depths and angles, they can be strategically placed to target specific preferential pathways more effectively. Additionally, their ability to treat a larger volume of groundwater with a single well can decrease the footprint of the remediation project, minimizing disturbance to the surrounding environment.
Case Study: Saprolite in Asheboro, NC
Directional Technologies installed one horizontal air sparge (HAS) well and one horizontal soil vapor extraction (HSVE) well beneath a manufacturing building for a pilot test in Asheboro, North Carolina. The Piedmont geographical region in North Carolina is mostly underlain by saprolite, a clay-rich soil formed by the in-place weathering of igneous and metamorphic bedrock. Due to its low permeability and high heterogeneity, saprolite is routinely a challenging substrate for in-situ remediation of soil and groundwater contamination. Utilizing vertical wells in saprolite conditions would have produced non-uniform ROIs, resulting in a failure to develop sound communication between wells and an incomplete capture zone.
By implementing horizontal SVE wells, there was an immediate success in reducing the moisture content in the soil within the vadose zone, gradually creating air movement through the former fractures of the weathered bedrock. Additionally, the horizontal air sparging successfully developed a radius of influence within the preferential pathways of the heterogeneric saprolite. Successful results of the pilot testing proved the air movement from the remedial system would infiltrate the same pathways that the trichloroethylene (TCE) impacted groundwater followed. Pilot study results culminated in the development of a full-scale remedial design. By implementing horizontal remediation wells, Directional Technologies was able to fully capture the migrating TCE plume, preventing downgradient migration into a nearby stream.
Conclusion
Horizontal remediation wells offer a superior advantage over vertical wells in groundwater remediation due to their ability to provide a more continuous radius of influence. This characteristic allows for better contact with the contaminant plume, ensures uniform cleanup progress, and promotes a more efficient and cost-effective remediation process. Their flexibility in installation and ability to navigate complex subsurface conditions make horizontal remediation wells a valuable tool for addressing subsurface contamination and restoring the quality of groundwater resources.
How can the advantages offered by decades of technological advancement in the field of horizontal wells benefit your project? Call our horizontal remediation well experts at 1-877-788-4479 to discuss your current project needs, or click HERE to complete our online form.
Written by: Elliott Andelman, Environmental Scientist